以太坊区块交易,虚拟机,合约源码分析视频教程
能学到什么
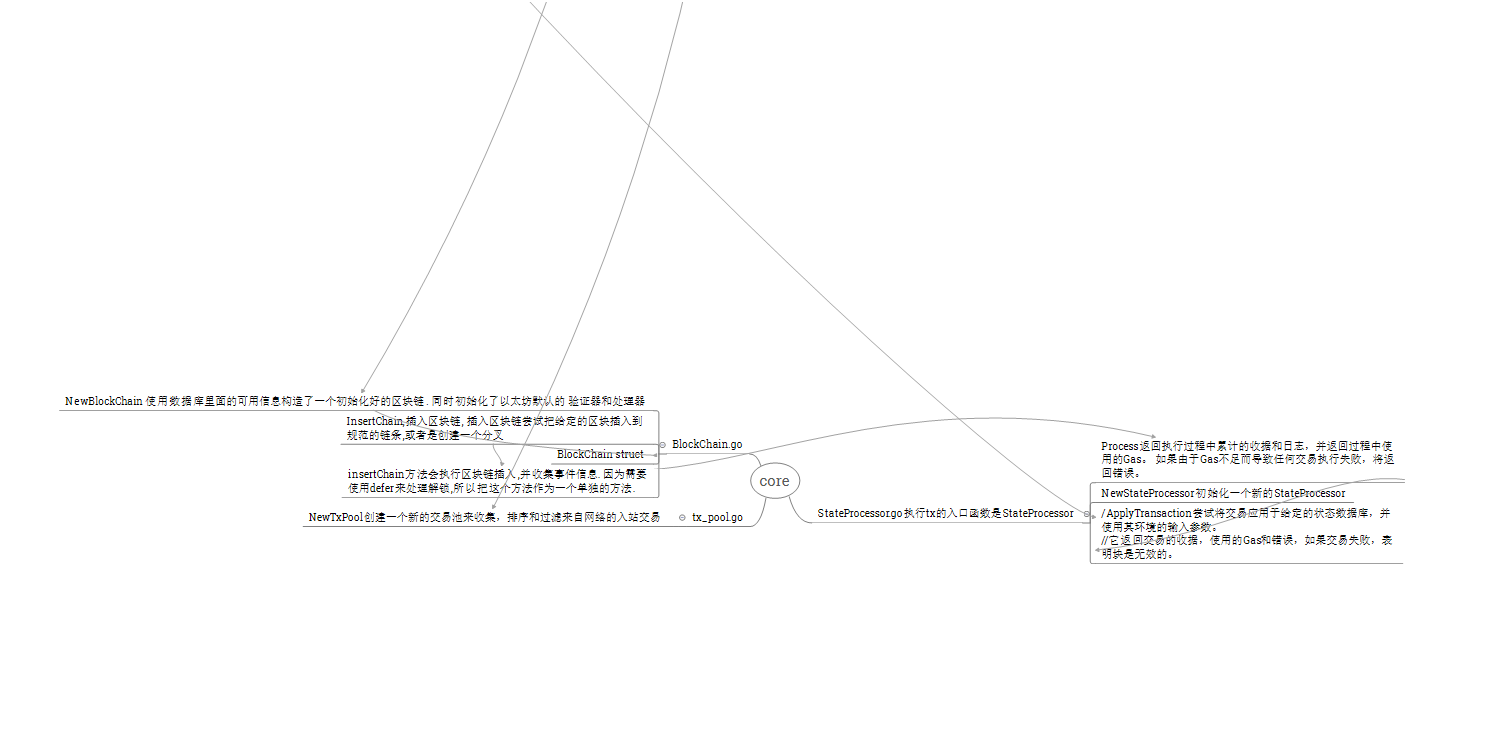
1.谁发起了交易?
blockchain.go里的insertChain(方法会执行区块链插入,并收集事件信息)
2交易有哪些种?交易在哪里执行?
一虚拟机外,执行前将Transaction类型转化成Message,创建evm虚拟机,计算交易gas。返回交易收据。
二虚拟机内,执行交易,创建合约,执行合约指令。
3区块的结构是什么样子的?
参考源码
4怎样打包区块写入区块链数据库
挖矿打包参看源码
5合约怎样执行?
一编译后直接执行,有两个函数,计算gas消耗,运行预编译的合约
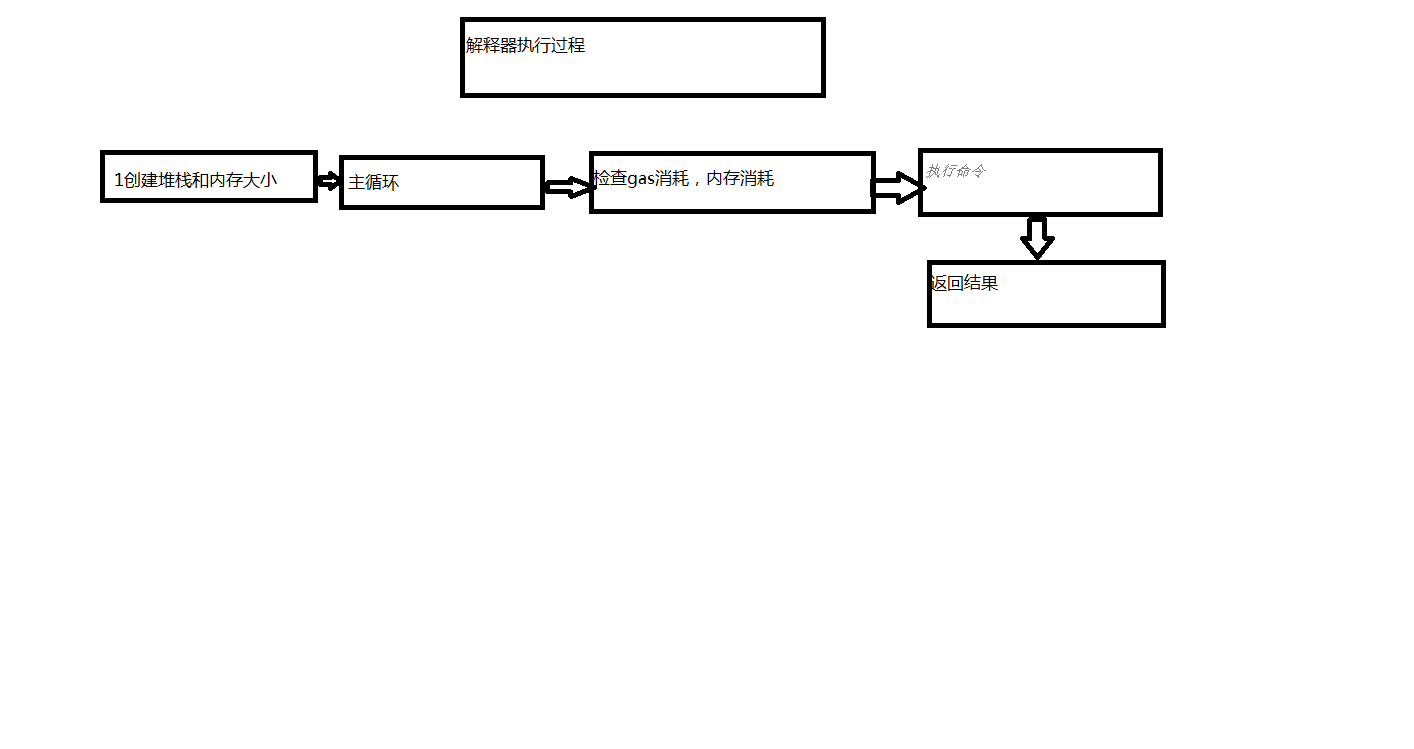
二通过解释器运行合约,解释器有4个函数,执行函数,计算gas消耗函数,计算堆栈大小函数,计算内存大小函数。
什么是区块,区块链?
区块是一个结构体,在以太坊里包含区块头,叔块头,交易列表
package core
import (
"math/big"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/common"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/consensus"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/core/types"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/core/vm"
)
// ChainContext支持从交易处理过程中使用的当前区块链中检索标题和共识参数。
// ChainContext supports retrieving headers and consensus parameters from the
// current blockchain to be used during transaction processing.
type ChainContext interface {
//引擎检索链的共识引擎。
// Engine retrieves the chain's consensus engine.
Engine() consensus.Engine
// GetHeader返回与它们的哈希对应的哈希。
// GetHeader returns the hash corresponding to their hash.
GetHeader(common.Hash, uint64) *types.Header
}
// NewEVMContext创建一个新的上下文以用于EVM。
// NewEVMContext creates a new context for use in the EVM.
func NewEVMContext(msg Message, header *types.Header, chain ChainContext, author *common.Address) vm.Context {
// If we don't have an explicit author (i.e. not mining), extract from the header
//如果我们没有明确的作者(即不是挖掘),请从标题中提取
var beneficiary common.Address
if author == nil {
beneficiary, _ = chain.Engine().Author(header) // Ignore error, we're past header validation
} else {
beneficiary = *author
}
return vm.Context{
CanTransfer: CanTransfer,
Transfer: Transfer,
GetHash: GetHashFn(header, chain),
Origin: msg.From(),
Coinbase: beneficiary,
BlockNumber: new(big.Int).Set(header.Number),
Time: new(big.Int).Set(header.Time),
Difficulty: new(big.Int).Set(header.Difficulty),
GasLimit: header.GasLimit,
GasPrice: new(big.Int).Set(msg.GasPrice()),
}
}
// GetHashFn返回一个GetHashFunc,它通过数字来检索头部哈希值
// GetHashFn returns a GetHashFunc which retrieves header hashes by number
func GetHashFn(ref *types.Header, chain ChainContext) func(n uint64) common.Hash {
return func(n uint64) common.Hash {
for header := chain.GetHeader(ref.ParentHash, ref.Number.Uint64()-1); header != nil; header = chain.GetHeader(header.ParentHash, header.Number.Uint64()-1) {
if header.Number.Uint64() == n {
return header.Hash()
}
}
return common.Hash{}
}
}
//可以转账检查地址帐户中是否有足够的资金进行转帐。
//这并没有采取必要的措施来确保传输的有效性。
// CanTransfer checks wether there are enough funds in the address' account to make a transfer.
// This does not take the necessary gas in to account to make the transfer valid.
func CanTransfer(db vm.StateDB, addr common.Address, amount *big.Int) bool {
return db.GetBalance(addr).Cmp(amount) >= 0
}
//传输从发件人中扣除金额,并使用给定的Db向收件人添加金额
// Transfer subtracts amount from sender and adds amount to recipient using the given Db
func Transfer(db vm.StateDB, sender, recipient common.Address, amount *big.Int) {
db.SubBalance(sender, amount)
db.AddBalance(recipient, amount)
// Copyright 2014 The go-ethereum Authors
// This file is part of the go-ethereum library.
//
// The go-ethereum library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
// it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by
// the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
// (at your option) any later version.
//
// The go-ethereum library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
// but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
// MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
// GNU Lesser General Public License for more details.
//
// You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
// along with the go-ethereum library. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
package vm
import (
"math/big"
"sync/atomic"
"time"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/common"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/crypto"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/params"
)
// emptyCodeHash由create使用,以确保不会部署已部署的合同地址(在帐户抽象后相关)。
// emptyCodeHash is used by create to ensure deployment is disallowed to already
// deployed contract addresses (relevant after the account abstraction).
var emptyCodeHash = crypto.Keccak256Hash(nil)
type (
CanTransferFunc func(StateDB, common.Address, *big.Int) bool
TransferFunc func(StateDB, common.Address, common.Address, *big.Int)
// GetHashFunc returns the nth block hash in the blockchain
// and is used by the BLOCKHASH EVM op code.
// GetHashFunc返回区块链中的第n个块哈希,并由BLOCKHASH EVM操作码使用。
GetHashFunc func(uint64) common.Hash
)
//EVM中执行合约(指令)的函数是run()
// run runs the given contract and takes care of running precompiles with a fallback to the byte code interpreter.
func run(evm *EVM, contract *Contract, input []byte) ([]byte, error) {
//可见如果待执行的Contract对象恰好属于一组预编译的合约集合-此时以指令地址CodeAddr为匹配项-那么它可以直接运行;
// 没有经过预编译的Contract,才会由Interpreter解释执行。
// 这里的"预编译",可理解为不需要编译(解释)指令(Code)。预编译的合约,其逻辑全部固定且已知,所以执行中不再需要Code,仅需Input即可。
if contract.CodeAddr != nil {
precompiles := PrecompiledContractsHomestead
if evm.ChainConfig().IsByzantium(evm.BlockNumber) {
precompiles = PrecompiledContractsByzantium
}
if p := precompiles[*contract.CodeAddr]; p != nil {//在代码实现中,预编译合约只需实现两个方法Required()和Run()即可,这两方法仅需一个入参input
return RunPrecompiledContract(p, input, contract)
}
}
return evm.interpreter.Run(contract, input)//解释器Interpreter用来执行(非预编译的)合约指令
}
// 上下文为EVM提供辅助信息。 一旦提供,不应该修改。
// Context provides the EVM with auxiliary information. Once provided
// it shouldn't be modified.
type Context struct {
// CanTransfer returns whether the account contains
// sufficient ether to transfer the value
CanTransfer CanTransferFunc// CanTransfer 函数返回账户是否有足够的ether用来转账
// Transfer transfers ether from one account to the other
Transfer TransferFunc// Transfer 用来从一个账户给另一个账户转账
// GetHash returns the hash corresponding to n
GetHash GetHashFunc// GetHash用来返回入参n对应的hash值
// Message information
Origin common.Address // Provides information for ORIGIN// 用来提供Origin的信息 sender的地址
GasPrice *big.Int // Provides information for GASPRICE// 用来提供GasPrice信息
// Block information
Coinbase common.Address // Provides information for COINBASE
GasLimit uint64 // Provides information for GASLIMIT
BlockNumber *big.Int // Provides information for NUMBER
Time *big.Int // Provides information for TIME
Difficulty *big.Int // Provides information for DIFFICULTY
}
// EVM is the Ethereum Virtual Machine base object and provides
// the necessary tools to run a contract on the given state with
// the provided context. It should be noted that any error
// generated through any of the calls should be considered a
// revert-state-and-consume-all-gas operation, no checks on
// specific errors should ever be performed. The interpreter makes
// sure that any errors generated are to be considered faulty code.
//// EVM是以太坊虚拟机基础对象,并提供必要的工具,以使用提供的上下文运行给定状态的合约。
// 应该指出的是,任何调用产生的任何错误都应该被认为是一种回滚修改状态和消耗所有GAS操作,
// 不应该执行对具体错误的检查。 解释器确保生成的任何错误都被认为是错误的代码。
// The EVM should never be reused and is not thread safe.
type EVM struct {
// Context provides auxiliary blockchain related information
Context//携带了Transaction的信息(GasPrice, GasLimit),Block的信息(Number, Difficulty),以及转帐函数等
// StateDB gives access to the underlying state
StateDB StateDB//tateDB 接口是针对state.StateDB 结构体设计的本地行为接口,可为EVM提供statedb的相关操作
// Depth is the current call stack
// 当前的调用堆栈
depth int
// chainConfig contains information about the current chain
// 包含了当前的区块链的信息
chainConfig *params.ChainConfig
//链规则包含当前时期的链规则
// chain rules contains the chain rules for the current epoch
chainRules params.Rules
//用于初始化evm的虚拟机配置选项。
// virtual machine configuration options used to initialise the
// evm.
vmConfig Config
//全局(在此上下文中)在整个tx执行过程中使用的以太坊虚拟机。
// global (to this context) ethereum virtual machine
// used throughout the execution of the tx.
interpreter *Interpreter// Interpreter结构体作为解释器,用来解释执行EVM中合约(Contract)的指令(Code)。
//中止用于中止EVM调用操作
//注意:必须以原子方式设置
// abort is used to abort the EVM calling operations
// NOTE: must be set atomically
abort int32
// callGasTemp保存当前通话可用的gas。 这是必要的,因为可用气体是根据63/64规则在gasCall *中计算的,稍后在opCall *中应用。
// callGasTemp holds the gas available for the current call. This is needed because the
// available gas is calculated in gasCall* according to the 63/64 rule and later
// applied in opCall*.
callGasTemp uint64
}
// NewEVM重新构建新的EVM。 返回的EVM不是线程安全的,应该只能使用*一次*。
// NewEVM retutrns a new EVM . The returned EVM is not thread safe and should
// only ever be used *once*.
func NewEVM(ctx Context, statedb StateDB, chainConfig *params.ChainConfig, vmConfig Config) *EVM {
evm := &EVM{
Context: ctx,
StateDB: statedb,
vmConfig: vmConfig,
chainConfig: chainConfig,
chainRules: chainConfig.Rules(ctx.BlockNumber),
}
evm.interpreter = NewInterpreter(evm, vmConfig)
return evm
}
//取消任何正在运行的EVM操作。 这可以同时调用,并且多次调用是安全的。
// Cancel cancels any running EVM operation. This may be called concurrently and
// it's safe to be called multiple times.
func (evm *EVM) Cancel() {
atomic.StoreInt32(&evm.abort, 1)
}
//Call方法, 无论我们转账或者是执行合约代码都会调用到这里, 同时合约里面的call指令也会执行到这里。
// Call executes the contract associated with the addr with the given input as
// parameters. It also handles any necessary value transfer required and takes
// the necessary steps to create accounts and reverses the state in case of an
// execution error or failed value transfer.
// Call 执行与给定的input作为参数与addr相关联的合约。
// 它还处理所需的任何必要的转账操作,并采取必要的步骤来创建帐户
// 并在任意错误的情况下回滚所做的操作。
func (evm *EVM) Call(caller ContractRef, addr common.Address, input []byte, gas uint64, value *big.Int) (ret []byte, leftOverGas uint64, err error) {
//1检查交易
if evm.vmConfig.NoRecursion && evm.depth > 0 {
return nil, gas, nil
}
// 调用深度最多1024
// Fail if we're trying to execute above the call depth limit
if evm.depth > int(params.CallCreateDepth) {
return nil, gas, ErrDepth
}
// 查看我们的账户是否有足够的金钱。
// Fail if we're trying to transfer more than the available balance
if !evm.Context.CanTransfer(evm.StateDB, caller.Address(), value) {
return nil, gas, ErrInsufficientBalance
}
var (
to = AccountRef(addr)
snapshot = evm.StateDB.Snapshot()
)
if !evm.StateDB.Exist(addr) {// 查看指定地址是否存在
// 如果地址不存在,查看是否是 native go的合约, native go的合约在
// contracts.go 文件里面
precompiles := PrecompiledContractsHomestead
if evm.ChainConfig().IsByzantium(evm.BlockNumber) {
precompiles = PrecompiledContractsByzantium
}
if precompiles[addr] == nil && evm.ChainConfig().IsEIP158(evm.BlockNumber) && value.Sign() == 0 {
// 如果不是指定的合约地址, 并且value的值为0那么返回正常,而且这次调用没有消耗Gas
return nil, gas, nil
}
// 负责在本地状态创建addr
evm.StateDB.CreateAccount(addr)
}
// 2执行转账
evm.Transfer(evm.StateDB, caller.Address(), to.Address(), value)
// Initialise a new contract and set the code that is to be used by the EVM.
// The contract is a scoped environment for this execution context only.
//3创建一个Contract对象,并初始化其成员变量caller, self(addr), value和gas
contract := NewContract(caller, to, value, gas)
//4赋值Contract对象的Code, CodeHash, CodeAddr成员变量
contract.SetCallCode(&addr, evm.StateDB.GetCodeHash(addr), evm.StateDB.GetCode(addr))
start := time.Now()
//以调试模式捕获跟踪器开始/结束事件
// Capture the tracer start/end events in debug mode
if evm.vmConfig.Debug && evm.depth == 0 {
evm.vmConfig.Tracer.CaptureStart(caller.Address(), addr, false, input, gas, value)
defer func() { // Lazy evaluation of the parameters//懒加载的参数评估
evm.vmConfig.Tracer.CaptureEnd(ret, gas-contract.Gas, time.Since(start), err)
}()
}
//5调用run()函数执行该合约的指令,最后Call()函数返回
ret, err = run(evm, contract, input)
//当EVM返回错误或设置上述创建代码时,我们恢复快照并消耗剩余的气体。 另外,当我们在家园时,这也代表了代码存储瓦斯错误。
// When an error was returned by the EVM or when setting the creation code
// above we revert to the snapshot and consume any gas remaining. Additionally
// when we're in homestead this also counts for code storage gas errors.
if err != nil {
evm.StateDB.RevertToSnapshot(snapshot)
if err != errExecutionReverted {
// 如果是由revert指令触发的错误,因为ICO一般设置了人数限制或者资金限制
// 在大家抢购的时候很可能会触发这些限制条件,导致被抽走不少钱。这个时候
// 又不能设置比较低的GasPrice和GasLimit。因为要速度快。
// 那么不会使用剩下的全部Gas,而是只会使用代码执行的Gas
// 不然会被抽走 GasLimit *GasPrice的钱,那可不少。
contract.UseGas(contract.Gas)
}
}
return ret, contract.Gas, err
}
//剩下的三个函数 CallCode, DelegateCall, 和 StaticCall,这三个函数不能由外部调用,只能由Opcode触发。
// CallCode executes the contract associated with the addr with the given input
// as parameters. It also handles any necessary value transfer required and takes
// the necessary steps to create accounts and reverses the state in case of an
// execution error or failed value transfer.
//// CallCode与Call不同的地方在于它使用caller的context来执行给定地址的代码。
// CallCode differs from Call in the sense that it executes the given address'
// code with the caller as context.
func (evm *EVM) CallCode(caller ContractRef, addr common.Address, input []byte, gas uint64, value *big.Int) (ret []byte, leftOverGas uint64, err error) {
if evm.vmConfig.NoRecursion && evm.depth > 0 {
return nil, gas, nil
}
//如果我们试图在通话深度限制以上执行,则会失败
// Fail if we're trying to execute above the call depth limit
if evm.depth > int(params.CallCreateDepth) {
return nil, gas, ErrDepth
}//如果我们尝试传输的可用余额超过了,则失败
// Fail if we're trying to transfer more than the available balance
if !evm.CanTransfer(evm.StateDB, caller.Address(), value) {
return nil, gas, ErrInsufficientBalance
}
var (
snapshot = evm.StateDB.Snapshot()
to = AccountRef(caller.Address())//这里是最不同的地方 to的地址被修改为caller的地址了 而且没有转账的行为
)
//初始化一个新的契约并设置E将使用的代码该契约是一个仅限于此执行上下文的作用域解释。
// initialise a new contract and set the code that is to be used by the
// E The contract is a scoped evmironment for this execution context
// only.
contract := NewContract(caller, to, value, gas)
contract.SetCallCode(&addr, evm.StateDB.GetCodeHash(addr), evm.StateDB.GetCode(addr))
ret, err = run(evm, contract, input)
if err != nil {
evm.StateDB.RevertToSnapshot(snapshot)
if err != errExecutionReverted {
contract.UseGas(contract.Gas)
}
}
return ret, contract.Gas, err
}
// DelegateCall 和 CallCode不同的地方在于 caller被设置为 caller的caller
// DelegateCall executes the contract associated with the addr with the given input
// as parameters. It reverses the state in case of an execution error.
//
// DelegateCall differs from CallCode in the sense that it executes the given address'
// code with the caller as context and the caller is set to the caller of the caller.
// DelegateCall以给定输入作为参数执行与addr关联的合同。 它在执行错误的情况下反转状态。
// DelegateCall与CallCode的不同之处在于,它以呼叫者作为上下文执行给定地址的代码,并将呼叫者设置为呼叫者的调用者。
func (evm *EVM) DelegateCall(caller ContractRef, addr common.Address, input []byte, gas uint64) (ret []byte, leftOverGas uint64, err error) {
if evm.vmConfig.NoRecursion && evm.depth > 0 {
return nil, gas, nil
}
// Fail if we're trying to execute above the call depth limit
if evm.depth > int(params.CallCreateDepth) {
return nil, gas, ErrDepth
}
var (
snapshot = evm.StateDB.Snapshot()
to = AccountRef(caller.Address())
)
// 标识为AsDelete()
// Initialise a new contract and make initialise the delegate values//初始化一个新的合约并初始化委托值
contract := NewContract(caller, to, nil, gas).AsDelegate()
contract.SetCallCode(&addr, evm.StateDB.GetCodeHash(addr), evm.StateDB.GetCode(addr))
ret, err = run(evm, contract, input)
if err != nil {
evm.StateDB.RevertToSnapshot(snapshot)
if err != errExecutionReverted {
contract.UseGas(contract.Gas)
}
}
return ret, contract.Gas, err
}
// StaticCall执行与给定输入的addr相关联的合同作为参数,同时禁止在调用期间对状态进行任何修改。
//试图执行此类修改的操作码将导致异常,而不是执行修改。
// StaticCall executes the contract associated with the addr with the given input
// as parameters while disallowing any modifications to the state during the call.
// Opcodes that attempt to perform such modifications will result in exceptions
// instead of performing the modifications.
// StaticCall不允许执行任何修改状态的操作,
func (evm *EVM) StaticCall(caller ContractRef, addr common.Address, input []byte, gas uint64) (ret []byte, leftOverGas uint64, err error) {
if evm.vmConfig.NoRecursion && evm.depth > 0 {
return nil, gas, nil
}
//如果我们试图在通话深度限制以上执行,则会失败
// Fail if we're trying to execute above the call depth limit
if evm.depth > int(params.CallCreateDepth) {
return nil, gas, ErrDepth
}
//确保readonly只在我们不是只读的时候才被设置,但是这也确保readonly标志不会被删除以用于子调用。
// Make sure the readonly is only set if we aren't in readonly yet
// this makes also sure that the readonly flag isn't removed for
// child calls.
if !evm.interpreter.readOnly {
evm.interpreter.readOnly = true
defer func() { evm.interpreter.readOnly = false }()
}
var (
to = AccountRef(addr)
snapshot = evm.StateDB.Snapshot()
)
//初始化一个新的合约并设置EVM使用的代码。 该合同仅限于此执行上下文的作用域环境。
// Initialise a new contract and set the code that is to be used by the
// EVM. The contract is a scoped environment for this execution context
// only.
contract := NewContract(caller, to, new(big.Int), gas)
contract.SetCallCode(&addr, evm.StateDB.GetCodeHash(addr), evm.StateDB.GetCode(addr))
//当EVM返回错误或设置上述创建代码时,我们恢复快照并消耗剩余的气体。 另外,当我们在Homestead时,这也代表了代码存储瓦斯错误。
// When an error was returned by the EVM or when setting the creation code
// above we revert to the snapshot and consume any gas remaining. Additionally
// when we're in Homestead this also counts for code storage gas errors.
ret, err = run(evm, contract, input)
if err != nil {
evm.StateDB.RevertToSnapshot(snapshot)
if err != errExecutionReverted {
contract.UseGas(contract.Gas)
}
}
return ret, contract.Gas, err
}
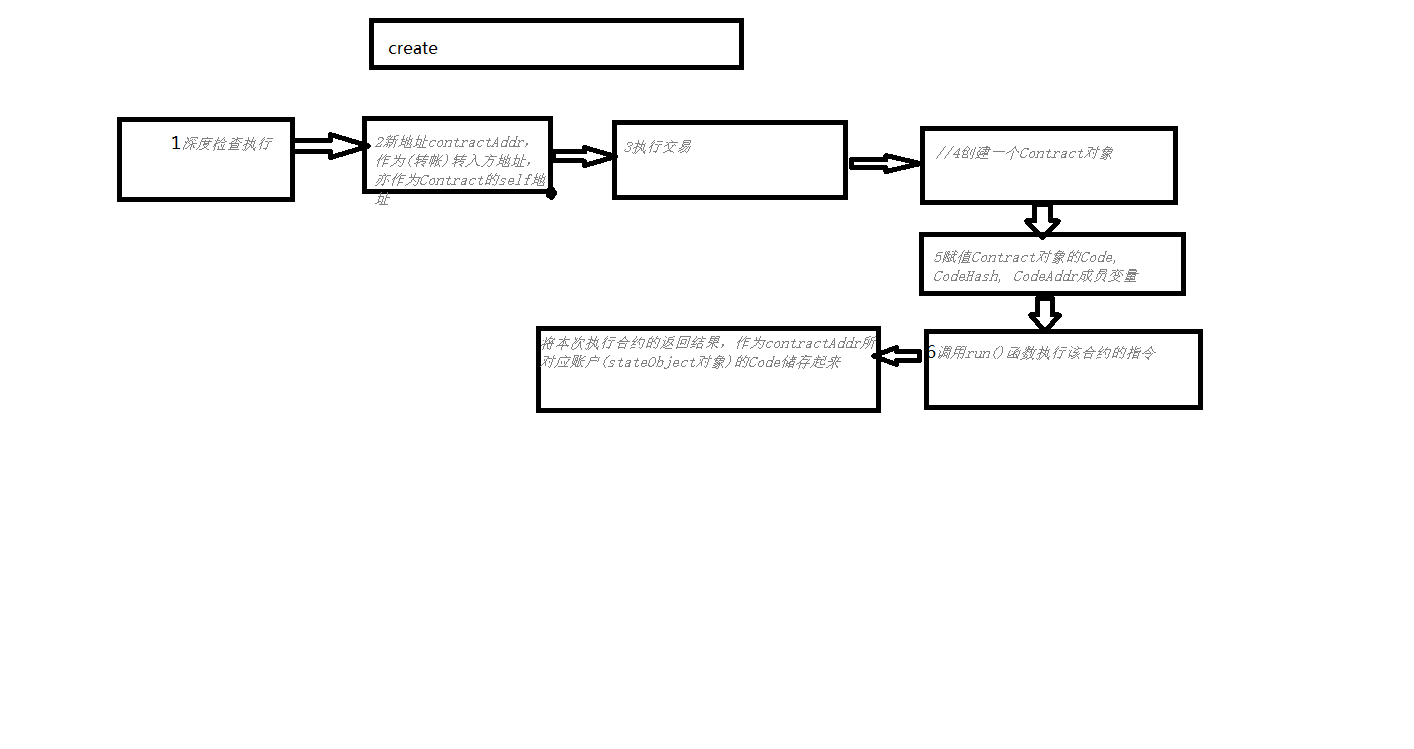
//合约创建 Create 会创建一个新的合约。
// Create creates a new contract using code as deployment code.
func (evm *EVM) Create(caller ContractRef, code []byte, gas uint64, value *big.Int) (ret []byte, contractAddr common.Address, leftOverGas uint64, err error) {
//1检查交易
// Depth check execution. Fail if we're trying to execute above the
// limit.
//深度检查执行。 如果我们试图超出限制执行失败。
if evm.depth > int(params.CallCreateDepth) {
return nil, common.Address{}, gas, ErrDepth
}
if !evm.CanTransfer(evm.StateDB, caller.Address(), value) {
return nil, common.Address{}, gas, ErrInsufficientBalance
}
// 确保特定的地址没有合约存在
// Ensure there's no existing contract already at the designated address
nonce := evm.StateDB.GetNonce(caller.Address())
evm.StateDB.SetNonce(caller.Address(), nonce+1)
//2新地址contractAddr,作为(转帐)转入方地址,亦作为Contract的self地址;
contractAddr = crypto.CreateAddress(caller.Address(), nonce)
contractHash := evm.StateDB.GetCodeHash(contractAddr)
if evm.StateDB.GetNonce(contractAddr) != 0 || (contractHash != (common.Hash{}) && contractHash != emptyCodeHash) {
return nil, common.Address{}, 0, ErrContractAddressCollision
}
// Create a new account on the state
snapshot := evm.StateDB.Snapshot()//创建一个StateDB的快照,以便回滚
evm.StateDB.CreateAccount(contractAddr)//创建账户
if evm.ChainConfig().IsEIP158(evm.BlockNumber) {
evm.StateDB.SetNonce(contractAddr, 1)//设置nonce
}
//3执行交易
evm.Transfer(evm.StateDB, caller.Address(), contractAddr, value)//转账
//初始化一个新的契约并设置E将使用的代码该契约是一个仅限于此执行上下文的作用域解释。
// initialise a new contract and set the code that is to be used by the
// E The contract is a scoped evmironment for this execution context
// only.
//4创建一个Contract对象,并初始化其成员变量caller, self(addr), value和ga
contract := NewContract(caller, AccountRef(contractAddr), value, gas)
//)5赋值Contract对象的Code, CodeHash, CodeAddr成员变量//db中尚无与该地址相关的Code信息,所以会将类型为[]byte的入参code,赋值予Contract对象的Code成员
contract.SetCallCode(&contractAddr, crypto.Keccak256Hash(code), code)
if evm.vmConfig.NoRecursion && evm.depth > 0 {
return nil, contractAddr, gas, nil
}
if evm.vmConfig.Debug && evm.depth == 0 {
evm.vmConfig.Tracer.CaptureStart(caller.Address(), contractAddr, true, code, gas, value)
}
start := time.Now()
//6调用run()函数执行该合约的指令
ret, err = run(evm, contract, nil) //执行合约的初始化代码
// 检查初始化生成的代码的长度不超过限制
// check whether the max code size has been exceeded
maxCodeSizeExceeded := evm.ChainConfig().IsEIP158(evm.BlockNumber) && len(ret) > params.MaxCodeSize
// if the contract creation ran successfully and no errors were returned
// calculate the gas required to store the code. If the code could not
// be stored due to not enough gas set an error and let it be handled
// by the error checking condition below.
//如果合同创建成功并且没有错误返回,则计算存储代码所需的GAS。 如果由于没有足够的GAS而导致代码不能被存储设置错误,并通过下面的错误检查条件来处理。
if err == nil && !maxCodeSizeExceeded {
createDataGas := uint64(len(ret)) * params.CreateDataGas
if contract.UseGas(createDataGas) {
evm.StateDB.SetCode(contractAddr, ret)
} else {
err = ErrCodeStoreOutOfGas
}
}
//当EVM返回错误或设置上述创建代码时,我们恢复快照并消耗剩余的气体。 另外,当我们在家园时,这也代表了代码存储瓦斯错误。
// When an error was returned by the EVM or when setting the creation code
// above we revert to the snapshot and consume any gas remaining. Additionally
// when we're in homestead this also counts for code storage gas errors.
// 当错误返回我们回滚修改,
if maxCodeSizeExceeded || (err != nil && (evm.ChainConfig().IsHomestead(evm.BlockNumber) || err != ErrCodeStoreOutOfGas)) {
evm.StateDB.RevertToSnapshot(snapshot)
if err != errExecutionReverted {
contract.UseGas(contract.Gas)
}
}//如果在err仍然为空时合同代码大小超过最大值,则分配err。
// Assign err if contract code size exceeds the max while the err is still empty.
if maxCodeSizeExceeded && err == nil {
err = errMaxCodeSizeExceeded
}
if evm.vmConfig.Debug && evm.depth == 0 {
evm.vmConfig.Tracer.CaptureEnd(ret, gas-contract.Gas, time.Since(start), err)
}
//7将本次执行合约的返回结果,作为contractAddr所对应账户(stateObject对象)的Code储存起来,以备下次调用。
return ret, contractAddr, contract.Gas, err
}
// ChainConfig返回环境的链配置
// ChainConfig returns the environment's chain configuration
func (evm *EVM) ChainConfig() *params.ChainConfig { return evm.chainConfig }
//解释器返回EVM解释器
// Interpreter returns the EVM interpreter
func (evm *EVM) Interpreter() *Interpreter { return evm.interpreter }
// Copyright 2015 The go-ethereum Authors
// This file is part of the go-ethereum library.
//
// The go-ethereum library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
// it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by
// the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
// (at your option) any later version.
//
// The go-ethereum library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
// but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
// MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
// GNU Lesser General Public License for more details.
//
// You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
// along with the go-ethereum library. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
package vm
import (
"math/big"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/common"
)
//contract 代表了以太坊 state database里面的一个合约。包含了合约代码,调用参数。
// ContractRef is a reference to the contract's backing object
// ContractRef是对合同支持对象的引用
type ContractRef interface {
Address() common.Address
}
// AccountRef实现ContractRef。
// EVM初始化期间使用帐户引用,主要用于获取地址。 删除这个对象证明是困难的,因为缓存的跳转目的地
//是从作为ContractRef的父合同(即调用者)获取的。
// AccountRef implements ContractRef.
//
// Account references are used during EVM initialisation and
// it's primary use is to fetch addresses. Removing this object
// proves difficult because of the cached jump destinations which
// are fetched from the parent contract (i.e. the caller), which
// is a ContractRef.
type AccountRef common.Address
// Address将AccountRef转换为地址
// Address casts AccountRef to a Address
func (ar AccountRef) Address() common.Address { return (common.Address)(ar) }
//合约代表状态数据库中的以太坊合约。 它包含合同代码,调用参数。 合同实施ContractRef
// Contract represents an ethereum contract in the state database. It contains
// the the contract code, calling arguments. Contract implements ContractRef
type Contract struct {
// CallerAddress是初始化此合同的调用者的结果。 但是,当“调用方法”被委托时,该值需要初始化为调用者的调用者的值。
// CallerAddress is the result of the caller which initialised this
// contract. However when the "call method" is delegated this value
// needs to be initialised to that of the caller's caller.
// CallerAddress是初始化这个合约的人。 如果是delegate,这个值被设置为调用者的调用者。
CallerAddress common.Address
caller ContractRef//caller是转帐转出方地址(账户)
self ContractRef//self是转入方地址
jumpdests destinations // result of JUMPDEST analysis. JUMPDEST指令的分析
Code []byte //代码,指令数组,其中每一个byte都对应于一个预定义的虚拟机指令
CodeHash common.Hash//代码的HASH,Code的RLP哈希值
CodeAddr *common.Address//代码地址
Input []byte // 入参,数据数组,是指令所操作的数据集合
Gas uint64// 合约还有多少Gas
value *big.Int
Args []byte//是参数
DelegateCall bool
}
// NewContract返回执行EVM的新合约环境
// NewContract returns a new contract environment for the execution of EVM.
func NewContract(caller ContractRef, object ContractRef, value *big.Int, gas uint64) *Contract {
c := &Contract{CallerAddress: caller.Address(), caller: caller, self: object, Args: nil}
if parent, ok := caller.(*Contract); ok {
// 如果 caller 是一个合约,说明是合约调用了我们。 jumpdests设置为caller的jumpdests
// Reuse JUMPDEST analysis from parent context if available.
c.jumpdests = parent.jumpdests
} else {
c.jumpdests = make(destinations)
}
// Gas should be a pointer so it can safely be reduced through the run
// This pointer will be off the state transition
c.Gas = gas
// ensures a value is set
c.value = value
return c
}
//AsDelegate将合约设置为委托调用并返回当前合同(用于链式调用)
// AsDelegate sets the contract to be a delegate call and returns the current
// contract (for chaining calls)
func (c *Contract) AsDelegate() *Contract {
c.DelegateCall = true
// NOTE: caller must, at all times be a contract. It should never happen
// that caller is something other than a Contract.
parent := c.caller.(*Contract)
c.CallerAddress = parent.CallerAddress
c.value = parent.value
return c
}
//GetOp 用来获取下一跳指令
// GetOp returns the n'th element in the contract's byte array
func (c *Contract) GetOp(n uint64) OpCode {
return OpCode(c.GetByte(n))
}
// GetByte returns the n'th byte in the contract's byte array
func (c *Contract) GetByte(n uint64) byte {
if n < uint64(len(c.Code)) {
return c.Code[n]
}
return 0
}
// Caller returns the caller of the contract.
//
// Caller will recursively call caller when the contract is a delegate
// call, including that of caller's caller.
func (c *Contract) Caller() common.Address {
return c.CallerAddress
}
//UseGas使用Gas。
// UseGas attempts the use gas and subtracts it and returns true on success
func (c *Contract) UseGas(gas uint64) (ok bool) {
if c.Gas < gas {
return false
}
c.Gas -= gas
return true
}
//当Contract对象作为一个ContractRef接口出现时,它返回的地址就是它的self地址
// Address returns the contracts address
func (c *Contract) Address() common.Address {
return c.self.Address()
}
// Value returns the contracts value (sent to it from it's caller)
func (c *Contract) Value() *big.Int {
return c.value
}
//SetCode ,SetCallCode 设置代码。
// SetCode sets the code to the contract
func (self *Contract) SetCode(hash common.Hash, code []byte) {
self.Code = code
self.CodeHash = hash
}
// SetCallCode sets the code of the contract and address of the backing data
// object
func (self *Contract) SetCallCode(addr *common.Address, hash common.Hash, code []byte) {
self.Code = code
self.CodeHash = hash
self.CodeAddr = addr
}
// Copyright 2015 The go-ethereum Authors
// This file is part of the go-ethereum library.
//
// The go-ethereum library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
// it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by
// the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
// (at your option) any later version.
//
// The go-ethereum library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
// but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
// MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
// GNU Lesser General Public License for more details.
//
// You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
// along with the go-ethereum library. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
package core
import (
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/common"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/consensus"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/consensus/misc"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/core/state"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/core/types"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/core/vm"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/crypto"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/params"
)
//执行tx的入口函数是StateProcessor的Process()函数
// StateProcessor is a basic Processor, which takes care of transitioning
// state from one point to another.
//StateTransition是用来处理一个一个的交易的。那么StateProcessor就是用来处理区块级别的交易的。
// StateProcessor implements Processor.
type StateProcessor struct {
config *params.ChainConfig // Chain configuration options
bc *BlockChain // Canonical block chain
engine consensus.Engine // Consensus engine used for block rewards
}
// NewStateProcessor初始化一个新的StateProcessor。
// NewStateProcessor initialises a new StateProcessor.
func NewStateProcessor(config *params.ChainConfig, bc *BlockChain, engine consensus.Engine) *StateProcessor {
return &StateProcessor{
config: config,
bc: bc,
engine: engine,
}
}
//Process,这个方法会被blockchain调用。
// Process processes the state changes according to the Ethereum rules by running
// the transaction messages using the statedb and applying any rewards to both
// the processor (coinbase) and any included uncles.
// Process 根据以太坊规则运行交易信息来对statedb进行状态改变,以及奖励挖矿者或者是其他的叔父节点。
// Process returns the receipts and logs accumulated during the process and
// returns the amount of gas that was used in the process. If any of the
// transactions failed to execute due to insufficient gas it will return an error.
// Process返回执行过程中累计的收据和日志,并返回过程中使用的Gas。 如果由于Gas不足而导致任何交易执行失败,将返回错误。
func (p *StateProcessor) Process(block *types.Block, statedb *state.StateDB, cfg vm.Config) (types.Receipts, []*types.Log, uint64, error) {
var (
receipts types.Receipts
usedGas = new(uint64)
header = block.Header()
allLogs []*types.Log
//GasPool对象是在一个Block执行开始时创建,并在该Block内所有tx的执行过程中共享,对于一个tx的执行可视为“全局”存储对象;
gp = new(GasPool).AddGas(block.GasLimit())//GasPool 类型其实就是big.Int。在一个Block的处理过程(即其所有tx的执行过程)中,GasPool 的值能够告诉你,剩下还有多少Gas可以使用。
// 在每一个tx执行过程中,Ethereum 还设计了偿退(refund)环节,所偿退的Gas数量也会加到这个GasPool里。
)
// Mutate the the block and state according to any hard-fork specs
// DAO 事件的硬分叉处理
if p.config.DAOForkSupport && p.config.DAOForkBlock != nil && p.config.DAOForkBlock.Cmp(block.Number()) == 0 {
misc.ApplyDAOHardFork(statedb)
}
//Process()函数的核心是一个for循环,它将Block里的所有tx逐个遍历执行。
// 具体的执行函数叫ApplyTransaction(),它每次执行tx, 会返回一个收据(Receipt)对象。
// Iterate over and process the individual transactions迭代并处理个人交易
for i, tx := range block.Transactions() {
statedb.Prepare(tx.Hash(), block.Hash(), i)//设置transaction hash 和block hash当前的交易的index
receipt, _, err := ApplyTransaction(p.config, p.bc, nil, gp, statedb, header, tx, usedGas, cfg)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, 0, err
}
receipts = append(receipts, receipt)
allLogs = append(allLogs, receipt.Logs...)
}//完成块,应用任何引擎特定的额外特性(例如块奖励)
// Finalize the block, applying any consensus engine specific extras (e.g. block rewards)
p.engine.Finalize(p.bc, header, statedb, block.Transactions(), block.Uncles(), receipts)
// 返回收据 日志 总的Gas使用量和nil
return receipts, allLogs, *usedGas, nil
}
//ApplyTransaction()首先根据输入参数分别封装出一个Message对象和一个EVM对象,然后加上一个传入的GasPool类型变量,由TransitionDb()函数完成tx的执行,
// 待TransitionDb()返回之后,创建一个收据Receipt对象,最后返回该Recetip对象,以及整个tx执行过程所消耗Gas数量。
// ApplyTransaction attempts to apply a transaction to the given state database
// and uses the input parameters for its environment. It returns the receipt
// for the transaction, gas used and an error if the transaction failed,
// indicating the block was invalid.
//ApplyTransaction尝试将交易应用于给定的状态数据库,并使用其环境的输入参数。
//它返回交易的收据,使用的Gas和错误,如果交易失败,表明块是无效的。
func ApplyTransaction(config *params.ChainConfig, bc *BlockChain, author *common.Address, gp *GasPool, statedb *state.StateDB, header *types.Header, tx *types.Transaction, usedGas *uint64, cfg vm.Config) (*types.Receipt, uint64, error) {
// 把交易转换成Message
// 这里如何验证消息确实是Sender发送的。 TODO
// 1Message由此次待执行的tx对象转化而来,并携带了解析出的tx的(转帐)转出方地址,属于待处理的数据对象
msg, err := tx.AsMessage(types.MakeSigner(config, header.Number))
if err != nil {
return nil, 0, err
}
// Create a new context to be used in the EVM environment
// 每一个交易都创建了新的虚拟机环境。
context := NewEVMContext(msg, header, bc, author)
//创建一个新的环境,它包含有关事务和调用机制的所有相关信息。
// Create a new environment which holds all relevant information
// about the transaction and calling mechanisms.
//EVM 作为Ethereum世界里的虚拟机(Virtual Machine),作为此次tx的实际执行者,完成转帐和合约(Contract)的相关操作。
vmenv := vm.NewEVM(context, statedb, config, cfg)
//将交易应用到当前状态(包含在env中)
// Apply the transaction to the current state (included in the env)
_, gas, failed, err := ApplyMessage(vmenv, msg, gp)
if err != nil {
return nil, 0, err
}
// Update the state with pending changes
// 求得中间状态
var root []byte
if config.IsByzantium(header.Number) {
statedb.Finalise(true)
} else {
root = statedb.IntermediateRoot(config.IsEIP158(header.Number)).Bytes()
}
*usedGas += gas
// Create a new receipt for the transaction, storing the intermediate root and gas used by the tx
// based on the eip phase, we're passing wether the root touch-delete accounts.
// 创建一个收据, 用来存储中间状态的root, 以及交易使用的gas
receipt := types.NewReceipt(root, failed, *usedGas)
receipt.TxHash = tx.Hash()
receipt.GasUsed = gas
// if the transaction created a contract, store the creation address in the receipt.
// 如果是创建合约的交易.那么我们把创建地址存储到收据里面.
if msg.To() == nil {
receipt.ContractAddress = crypto.CreateAddress(vmenv.Context.Origin, tx.Nonce())
}
// Set the receipt logs and create a bloom for filtering
// 拿到所有的日志并创建日志的布隆过滤器.
receipt.Logs = statedb.GetLogs(tx.Hash())
receipt.Bloom = types.CreateBloom(types.Receipts{receipt})
return receipt, gas, err
}
// Copyright 2014 The go-ethereum Authors
// This file is part of the go-ethereum library.
//
// The go-ethereum library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
// it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by
// the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
// (at your option) any later version.
//
// The go-ethereum library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
// but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
// MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
// GNU Lesser General Public License for more details.
//
// You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
// along with the go-ethereum library. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
package core
import (
"errors"
"math"
"math/big"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/common"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/core/vm"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/log"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/params"
)
var (
errInsufficientBalanceForGas = errors.New("insufficient balance to pay for gas")
)
/*
The State Transitioning Model
状态转换模型
A state transition is a change made when a transaction is applied to the current world state
状态转换 是指用当前的world state来执行交易,并改变当前的world state
The state transitioning model does all all the necessary work to work out a valid new state root.
状态转换做了所有所需的工作来产生一个新的有效的state root
1) Nonce handling Nonce 处理
2) Pre pay gas 预先支付Gas
3) Create a new state object if the recipient is \0*32 如果接收人是空,那么创建一个新的state object
4) Value transfer 转账
== If contract creation ==
4a) Attempt to run transaction data 尝试运行输入的数据
4b) If valid, use result as code for the new state object 如果有效,那么用运行的结果作为新的state object的code
== end ==
5) Run Script section 运行脚本部分
6) Derive new state root 导出新的state root
*/
type StateTransition struct {
gp *GasPool //用来追踪区块内部的Gas的使用情况
msg Message // Message Call
gas uint64//gas表示即时可用Gas数量,初始值均为0
gasPrice *big.Int // gas的价格
initialGas *big.Int // 最开始的gas初始值均为0
value *big.Int // 转账的值
data []byte // 输入数据
state vm.StateDB // StateDB
evm *vm.EVM // 虚拟机
}
// Message represents a message sent to a contract.
type Message interface {
From() common.Address
//FromFrontier() (common.Address, error)
To() *common.Address
GasPrice() *big.Int
Gas() uint64
Value() *big.Int
Nonce() uint64
CheckNonce() bool
Data() []byte
}
//关于g0的计算,在黄皮书上由详细的介绍 和黄皮书有一定出入的部分在于if contractCreation && homestead
// {igas.SetUint64(params.TxGasContractCreation) 这是因为 Gtxcreate+Gtransaction = TxGasContractCreation
// IntrinsicGas computes the 'intrinsic gas' for a message with the given data.
func IntrinsicGas(data []byte, contractCreation, homestead bool) (uint64, error) {
// Set the starting gas for the raw transaction
var gas uint64
if contractCreation && homestead {
gas = params.TxGasContractCreation
} else {
gas = params.TxGas
}
//通过交易数据量来提取所需的气体
// Bump the required gas by the amount of transactional data
if len(data) > 0 {
// Zero and non-zero bytes are priced differently
//零和非零字节的价格不同
var nz uint64
for _, byt := range data {
if byt != 0 {
nz++
}
}
// Make sure we don't exceed uint64 for all data combinations
//确保所有数据组合都不超过uint64
if (math.MaxUint64-gas)/params.TxDataNonZeroGas < nz {
return 0, vm.ErrOutOfGas
}
gas += nz * params.TxDataNonZeroGas
z := uint64(len(data)) - nz
if (math.MaxUint64-gas)/params.TxDataZeroGas < z {
return 0, vm.ErrOutOfGas
}
gas += z * params.TxDataZeroGas
}
return gas, nil
}
// New State Transition initialises and returns a new state transition object.
// NewStateTransition初始化并返回一个新的状态转换对象。
// NewStateTransition initialises and returns a new state transition object.
func NewStateTransition(evm *vm.EVM, msg Message, gp *GasPool) *StateTransition {
return &StateTransition{
gp: gp,
evm: evm,
msg: msg,
gasPrice: msg.GasPrice(),
value: msg.Value(),
data: msg.Data(),
state: evm.StateDB,
}
}
// ApplyMessage computes the new state by applying the given message
// against the old state within the environment.
// ApplyMessage 通过应用给定的Message 和状态来生成新的状态
// ApplyMessage returns the bytes returned by any EVM execution (if it took place),
// the gas used (which includes gas refunds) and an error if it failed. An error always
// indicates a core error meaning that the message would always fail for that particular
// state and would never be accepted within a block.
// ApplyMessage返回由任何EVM执行(如果发生)返回的字节,
// 使用的Gas(包括Gas退款),如果失败则返回错误。 一个错误总是表示一个核心错误,
// 意味着这个消息对于这个特定的状态将总是失败,并且永远不会在一个块中被接受。
func ApplyMessage(evm *vm.EVM, msg Message, gp *GasPool) ([]byte, uint64, bool, error) {
return NewStateTransition(evm, msg, gp).TransitionDb()
}
func (st *StateTransition) from() vm.AccountRef {
f := st.msg.From()
if !st.state.Exist(f) {
st.state.CreateAccount(f)
}
return vm.AccountRef(f)
}
func (st *StateTransition) to() vm.AccountRef {
if st.msg == nil {
return vm.AccountRef{}
}
to := st.msg.To()
if to == nil {
return vm.AccountRef{} // contract creation
}
reference := vm.AccountRef(*to)
if !st.state.Exist(*to) {
st.state.CreateAccount(*to)
}
return reference
}
func (st *StateTransition) useGas(amount uint64) error {
if st.gas < amount {
return vm.ErrOutOfGas
}
st.gas -= amount
return nil
}
//buyGas, 实现Gas的预扣费, 首先就扣除你的GasLimit * GasPrice的钱。 然后根据计算完的状态在退还一部分。
func (st *StateTransition) buyGas() error {
var (
state = st.state
sender = st.from()
)
mgval := new(big.Int).Mul(new(big.Int).SetUint64(st.msg.Gas()), st.gasPrice)
if state.GetBalance(sender.Address()).Cmp(mgval) < 0 {
return errInsufficientBalanceForGas
}
if err := st.gp.SubGas(st.msg.Gas()); err != nil {// 从区块的gaspool里面减去, 因为区块是由GasLimit限制整个区块的Gas使用的。
return err
}
st.gas += st.msg.Gas()
st.initialGas = st.msg.Gas()
state.SubBalance(sender.Address(), mgval)
// 从账号里面减去 GasLimit * GasPrice
return nil
}
//执行前的检查
func (st *StateTransition) preCheck() error {
msg := st.msg
sender := st.from()
// Make sure this transaction's nonce is correct
if msg.CheckNonce() {
nonce := st.state.GetNonce(sender.Address())
// 当前本地的nonce 需要和 msg的Nonce一样 不然就是状态不同步了。
if nonce < msg.Nonce() {
return ErrNonceTooHigh
} else if nonce > msg.Nonce() {
return ErrNonceTooLow
}
}
return st.buyGas()
}
// TransitionDb将通过应用当前消息并返回包含使用过的气体的结果来转换状态。 如果失败,它会返回一个错误。 错误表示共识问题。
// TransitionDb will transition the state by applying the current message and
// returning the result including the the used gas. It returns an error if it
// failed. An error indicates a consensus issue.
func (st *StateTransition) TransitionDb() (ret []byte, usedGas uint64, failed bool, err error) {
if err = st.preCheck(); err != nil {//购买Gas。首先从交易的(转帐)转出方账户扣除一笔Ether,费用等于tx.data.GasLimit * tx.data.Price;
// 同时 st.initialGas = st.gas = tx.data.GasLimit;然后(GasPool) gp -= st.gas。
return
}
msg := st.msg
sender := st.from() // err checked in preCheck在检查前检查错误
homestead := st.evm.ChainConfig().IsHomestead(st.evm.BlockNumber)
contractCreation := msg.To() == nil // 如果msg.To是nil 那么认为是一个合约创建
// 计算最开始的Gas g0
// Pay intrinsic gas
//计算tx的固有Gas消耗 - intrinsicGas。它分为两个部分,每一个tx预设的消耗量,这个消耗量还因tx是否含有(转帐)转入方地址而略有不同;
// 以及针对tx.data.Payload的Gas消耗,Payload类型是[]byte,关于它的固有消耗依赖于[]byte中非0字节和0字节的长度。
// 最终,st.gas -= intrinsicGas
gas, err := IntrinsicGas(st.data, contractCreation, homestead)
if err != nil {
return nil, 0, false, err
}
if err = st.useGas(gas); err != nil {
return nil, 0, false, err
}
var (
evm = st.evm
// vm错误不会影响一致性,因此不会分配给err,除非平衡错误不足。
// vm errors do not effect consensus and are therefor
// not assigned to err, except for insufficient balance
// error.
vmerr error
)
//EVM执行。如果交易的(转帐)转入方地址(tx.data.Recipient)为空,调用EVM的Create()函数;
// 否则,调用Call()函数。无论哪个函数返回后,更新st.gas。
if contractCreation { //如果是合约创建, 那么调用evm的Create方法
ret, _, st.gas, vmerr = evm.Create(sender, st.data, st.gas, st.value)
} else {
// 如果是方法调用。那么首先设置sender的nonce。
// Increment the nonce for the next transaction
st.state.SetNonce(sender.Address(), st.state.GetNonce(sender.Address())+1)
ret, st.gas, vmerr = evm.Call(sender, st.to().Address(), st.data, st.gas, st.value)
}
if vmerr != nil {
log.Debug("VM returned with error", "err", vmerr)
//唯一可能的共识错误是如果没有足够的余额来完成转移, 第一笔余额转账可能永远不会失败。
// The only possible consensus-error would be if there wasn't
// sufficient balance to make the transfer happen. The first
// balance transfer may never fail.
if vmerr == vm.ErrInsufficientBalance {
return nil, 0, false, vmerr
}
}
//new(big.Int).Set(st.gasUsed()) 计算被使用的Gas数量
//4计算本次执行交易的实际Gas消耗: requiredGas = st.initialGas - st.gas
//偿退Gas。它包括两个部分:首先将剩余st.gas 折算成Ether,归还给交易的(转帐)转出方账户;然后,基于实际消耗量requiredGas,
// 系统提供一定的补偿,数量为refundGas。refundGas 所折算的Ether会被立即加在(转帐)转出方账户上,
// 同时st.gas += refundGas,gp += st.gas,即剩余的Gas加上系统补偿的Gas,被一起归并进GasPool,供之后的交易执行使用。
st.refundGas()//计算Gas的退费 会增加到 st.gas上面。 所以矿工拿到的是退税后的
//6奖励所属区块的挖掘者:系统给所属区块的作者,亦即挖掘者账户,增加一笔金额,数额等于 st.data,Price * (st.initialGas - st.gas)。
// 注意,这里的st.gas在步骤5中被加上了refundGas, 所以这笔奖励金所对应的Gas,其数量小于该交易实际消耗量requiredGas。
st.state.AddBalance(st.evm.Coinbase, new(big.Int).Mul(new(big.Int).SetUint64(st.gasUsed()), st.gasPrice))
//st.state.AddBalance(st.evm.Coinbase, new(big.Int).Mul(st.gasUsed(), st.gasPrice)) // 给矿工增加收入。
// requiredGas和gasUsed的区别一个是没有退税的, 一个是退税了的。
// 看上面的调用 ApplyMessage直接丢弃了requiredGas, 说明返回的是退税了的。
return ret, st.gasUsed(), vmerr != nil, err
}
//退税,退税是为了奖励大家运行一些能够减轻区块链负担的指令, 比如清空账户的storage. 或者是运行suicide命令来清空账号。
func (st *StateTransition) refundGas() {
//退税的总金额不会超过用户Gas总使用的1/2。
// Apply refund counter, capped to half of the used gas.
refund := st.gasUsed() / 2
if refund > st.state.GetRefund() {
refund = st.state.GetRefund()
}
st.gas += refund
//返回剩余气体的ETH,以原始速率交换。
// Return ETH for remaining gas, exchanged at the original rate.
sender := st.from()
remaining := new(big.Int).Mul(new(big.Int).SetUint64(st.gas), st.gasPrice)
// 用户还剩下的Gas还回去。
st.state.AddBalance(sender.Address(), remaining)
// Also return remaining gas to the block gas counter so it is
// available for the next transaction.
// 同时也把退税的钱还给gaspool给下个交易腾点Gas空间。
st.gp.AddGas(st.gas)
}
// gasUsed返回状态转换所用的气体量。
// gasUsed returns the amount of gas used up by the state transition.
func (st *StateTransition) gasUsed() uint64 {
return st.initialGas - st.gas
}
本文章版权归xiaowenwe@gmail.com所有,若想转载请联系作者授权,未经授权,禁止转载,如若发现,将通过个人律师以侵犯《中华人民共和国著作权法》起诉(奉陪到底),授权转载也请注明原出处。
赞助99元可以获得miner包完整Xmind,赞助199元可以获得miner包完整翻译源码,欢迎留言。按留言决定分析模块顺序。
更多精彩内容