用java写一个简单的区块链(上)
创建区块链
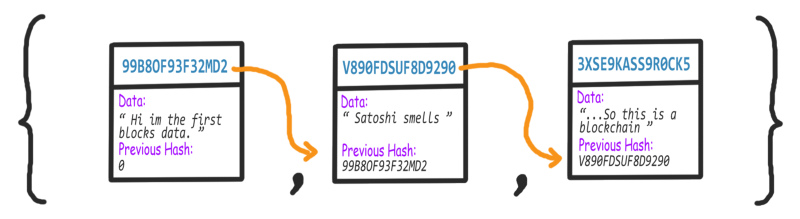
区块链就是一串或者是一系列区块的集合,类似于链表的概念,每个区块都指向于后面一个区块,然后顺序的连接在一起。那么每个区块中的内容是什么呢?在区块链中的每一个区块都存放了很多很有价值的信息,主要包括三个部分:自己的数字签名,上一个区块的数字签名,还有一切需要加密的数据(这些数据在比特币中就相当于是交易的信息,它是加密货币的本质)。每个数字签名不但证明了自己是特有的一个区块,而且指向了前一个区块的来源,让所有的区块在链条中可以串起来,而数据就是一些特定的信息,你可以按照业务逻辑来保存业务数据。
这里的hash指的就是数字签名
所以每一个区块不仅包含前一个区块的hash值,同时包含自身的一个hash值,自身的hash值是通过之前的hash值和数据data通过hash计算出来的。如果前一个区块的数据一旦被篡改了,那么前一个区块的hash值也会同样发生变化(因为数据也被计算在内),这样也就导致了所有后续的区块中的hash值。所以计算和比对hash值会让我们检查到当前的区块链是否是有效的,也就避免了数据被恶意篡改的可能性,因为篡改数据就会改变hash值并破坏整个区块链。
一、封装区块对象
package com.pibigstar.blockchain;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* 封装区块对象
* @author pibigstar
*
*/
public class Block {
public String hash;
//上一个区块的hash值
public String previousHash;
//每个区块存放的信息,这里我们存放的是一串字符串
private String data;
//时间戳
private long timeStamp;
//挖矿者的工作量证明
private int nonce;
//构造
public Block(String data,String previousHash ) {
this.data = data;
this.previousHash = previousHash;
this.timeStamp = new Date().getTime();
//根据previousHash、data和timeStamp产生唯一hash
this.hash = calculateHash();
}
//基于上一块的内容计算新的散列
public String calculateHash() {
String calculatedhash = StringUtil.applySha256(
previousHash +
Long.toString(timeStamp) +
Integer.toString(nonce) +
data
);
return calculatedhash;
}
//挖矿
public void mineBlock(int difficulty) {
//目标值,difficulty越大,下面计算量越大
String target = StringUtil.getDificultyString(difficulty);
//difficulty如果为5,那么target则为 00000
while(!hash.substring( 0, difficulty).equals(target)) {
nonce ++;
hash = calculateHash();
}
System.out.println("创建区块:" + hash);
}
}
二、封装工具类
package com.pibigstar.blockchain;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import com.google.gson.GsonBuilder;
/**
* 工具类
* 创建数字签名、返回JSON格式数据、返回难度字符串目标
* @author pibigstar
*
*/
public class StringUtil {
//将Sha256应用到一个字符串并返回结果
public static String applySha256(String input){
try {
MessageDigest digest = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256");
byte[] hash = digest.digest(input.getBytes("UTF-8"));
StringBuffer hexString = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < hash.length; i++) {
String hex = Integer.toHexString(0xff & hash[i]);
if(hex.length() == 1) hexString.append('0');
hexString.append(hex);
}
return hexString.toString();
}
catch(Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//返回JSON格式数据
public static String getJson(Object o) {
return new GsonBuilder().setPrettyPrinting().create().toJson(o);
}
//返回难度字符串目标,与散列比较。难度5将返回“00000”
public static String getDificultyString(int difficulty) {
return new String(new char[difficulty]).replace('\0', '0');
}
}
三、主函数,开始创建区块链
package com.pibigstar.blockchain;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import com.google.gson.GsonBuilder;
/**
* 创建区块链
* @author pibigstar
*
*/
public class BlockChain{
//存放所有的区块集合
public static ArrayList<Block> blockchain = new ArrayList<Block>();
public static int difficulty = 5;//挖矿的难度,数字越大越难
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("正在创建第一个区块链....... ");
addBlock(new Block("我是第一个区块链", "0"));//创世块
System.out.println("正在创建第二个区块链....... ");
addBlock(new Block("我是第二个区块链",blockchain.get(blockchain.size()-1).hash));
System.out.println("正在创建第三个区块链.......");
addBlock(new Block("我是第三个区块链",blockchain.get(blockchain.size()-1).hash));
System.out.println("区块链是否有效的: " + isChainValid());
String blockchainJson = StringUtil.getJson(blockchain);
System.out.println(blockchainJson);
}
/**
* 检查区块链的完整性
* @return
*/
public static Boolean isChainValid() {
Block currentBlock;
Block previousBlock;
String hashTarget = new String(new char[difficulty]).replace('\0', '0');
//循环区块链检查散列:
for(int i=1; i < blockchain.size(); i++) {
currentBlock = blockchain.get(i);
previousBlock = blockchain.get(i-1);
//比较注册散列和计算散列:
if(!currentBlock.hash.equals(currentBlock.calculateHash()) ){
System.out.println("Current Hashes not equal");
return false;
}
//比较以前的散列和注册的先前的散列
if(!previousBlock.hash.equals(currentBlock.previousHash) ) {
System.out.println("Previous Hashes not equal");
return false;
}
//检查哈希是否被使用
if(!currentBlock.hash.substring( 0, difficulty).equals(hashTarget)) {
System.out.println("这个区块还没有被开采。。。");
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* 增加一个新的区块
* @param newBlock
*/
public static void addBlock(Block newBlock) {
newBlock.mineBlock(difficulty);
blockchain.add(newBlock);
}
}
运行结果
更多精彩内容